You’ll never believe what I just found out about internal links. Sites with well-placed internal links can experience up to a 60% increase in website visitors. Knowing how to optimize your internal links for SEO is a game changer and can take your website to the next level.
According to Google, websites with internal links can have up to 150% more pages indexed by Google. Internal links are like traffic directors for your website and Googlebot loves it when your pages are well-connected.
Maybe you’re not sure how many links are too many, or you are worried about messing up your SEO game. This article will tackle common problems website owners face with internal linking and give you a clear understanding of how you can turn your website from trash to gold.
What is internal linking?
Internal linking is when you connect one page of a website to another on the same website. It makes website navigation easier, distributes the page rank (link juice) of a page around a website, and helps search engines find the important pages of a website.
These links are like pathways that help you explore more about a topic without leaving the website. They make jumping around and finding more interesting stuff on a website easy. Let’s say you are reading a blog about cats (main page), and there’s a link that says “Check out our favorite cat toys” (internal links). When you click that link, it takes you to the page about cat toys.
How to Optimize Your Internal Links for SEO
Internal link optimization is an important factor of SEO that helps search engines understand your website structure. Here are the best practices you can follow that will yield better ranking results for your website:
- When you link one page of your website to another, make sure they are related and it makes sense to link to it.
- The anchor text (clickable words) should tell visitors what to expect when they click on it. If it’s about cat pictures, the anchor text should be “cute cat pictures”
- Not all internal links are equal so ensure you link from new pages to old pages and vice-versa.
- Link related content together. If you are talking about clothes, link to other pages about clothes.
- Make sure that you don’t have any broken internal links as this is bad for SEO.
- Use keywords that people search for as anchor text and too many links on a page can hurt your page.
- Use link-building SEO tools to see which pages are performing best and link to them.
- You can use the “internal links” report under the section “Links” in Google Search Console tools to find out the status of your internal link building.
- Look at any Wikipedia page and notice how they use internal links and update links when you add new content.
Types of Internal Links
- Navigational Links

These links are mainly found in menus, sidebars, or a page's header. Navigational links are the signposts of a website, guiding you around and helping you find what you want. A navigational link can:
- Have clear and descriptive labels to show the content they lead to.
- Be consistent across different pages of a website.
- Provide a comprehensive overview of what the site offers.
- Visually different from regular text to draw attention
- Responsive to user’s needs by providing a clear path for visitors to explore various website sections.
- Easy accessible to all users especially those with disabilities. With features like proper labeling for screen readers.
2. Contextual Links
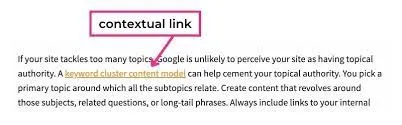
Contextual links are embedded links in relevant keywords. They are hyperlinks within content that point to other related content and help visitors know what to expect when they click the link. Search engines use contextual links to understand the relationship between pages on a website.
This type of internal link plays an important role in content optimization. Contextual links are valuable because they guide visitors to relevant information and increase the website's authority.
3. Footer Links
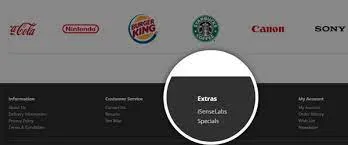
Links found at the bottom of a page are called footer links. The footer is the perfect place for links that cannot fit in the main navigation menu. For example, privacy policy, FAQ, and terms of service. Websites often include links to their social media profiles in the footer.
- Footer links can have links to features that allow users to adjust settings for a better experience.
- Long pages come with a “Back to Top” link which is found in the footer.
- Some websites have a condensed version of their site map in the footer that enables visitors to see the overall structure of the website.
- Contact details, copyright information, and legal disclaimers are found in the footer.
4. Breadcrumb Links
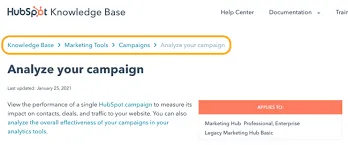
Breadcrumb links are clickable links that show you where you are on a website and how you got there. It is a digital path that guides you and lets you jump back to where you started without getting lost.
For example, if you are shopping online for shoes, the breadcrumbs could be “Home>Men’s Shoes>Running Shoes.” A breadcrumb link should have:
- Pathway indicators that show the path you took to arrive at a particular page.
- Hierarchical display within a website structure displays a page location.
- The first breadcrumb must link to the homepage and each part of the breadcrumb must be clickable.
- Breadcrumb links have a sequential order and are straightforward to understand.\
5. Image Links

Image links are clickable pictures on a website. People visiting the website can click on images to go to different pages instead of words. Image links make it fun and easy to explore content by simply clicking on interesting pictures.
This is a great way to keep users engaged on your website. If there’s a photo of a Labrador on your website, Labrador lovers will click on it to see more pictures about Labrador.
.
6. Call-to-Action (CTA) Links
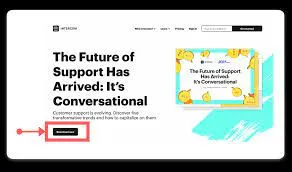
A CTA link is a button or text that prompts people to take action. It could be “Buy Now,” “Subscribe,” or “Learn More.” The CTA link guides visitors to the next step you want them to take whether it is signing up for a newsletter, making a purchase, or contacting you.
Here are the features of CTA links:
- Contains clear and persuasive words that tell visitors what will happen when they click on it.
- They are noticeable and easy to find because of their contrasting colors and bold fonts.
- They are placed where people are likely to see them and are related to the content around them.
- The language used in CTAs is action-oriented, encouraging users to take a specific action.
- CTAs are responsive on various devices and create a sense of urgency. For example, “Limited Time Offer”
- The design and language of CTA are the same as the brand’s style.
Conclusion
I have been a website owner for 7+ years and I can tell you how important internal links are to search engine rankings. By following the tips in this content, you can guide your visitors seamlessly through your content.
A well-optimized internal linking structure makes navigation easy for your website visitors and also lets search engines know the importance of the pages you link to. Remember to use link-building tools for insights and always improve your internal linking strategy.
FAQs
Why is internal linking important?
Internal linking improves user experience, optimizes navigation, and helps search engines understand the hierarchy of content. It can improve SEO and spread page authority as well.
How do I choose which pages to link internally?
Provide links to pages that lead readers naturally through your content or offer additional useful details. Give priority to pages that complement your website's general structure and the user's journey.
How many internal links should a page have?
There's no fixed number. Prioritize quality over quantity. Make sure every link has a function and is important to the information in its context.
Should I use dofollow or nofollow for internal links?
Internal links can usually be configured to follow. Dofollow links distribute link equity, which has a favorable effect on SEO. For links to pages that you do not want search engines to index or crawl, use nofollow instead.
Are there any common mistakes to avoid with internal linking?
Avoid overstuffing links on a page, using vague anchor text, or linking to irrelevant content. Also, ensure that your internal links are regularly audited and updated to reflect changes in your website's structure or content.




